Double Compression Cable Gland: An Introduction
When it comes to the safe and efficient installation of electrical cables, using the right cable gland is crucial. A cable gland is a device that secures the end of a cable to a piece of equipment or a junction box. Strain relief not only offers strain relief for cables, but it also serves to seal off electrical connections from moisture, dust, and other potential contaminants.
One type of cable gland that has recently gained attention is double compression cable glands. Here we will take a deeper look into their characteristics, how they operate, and their importance in modern electrical installations.
What is a Double Compression Cable Gland?
A double compression cable gland is a type of cable gland which uses two seals to provide a watertight seal around a cable, or conduit. The term double compression refers to this design which uses the first seal around its jacket while the second compresses against the inner sheath of cable.
Double compression cable glands offer several distinct advantages over their single counterparts, most notably providing additional moisture protection and guarding against contaminants that might compromise cable integrity in harsh environments with extreme temperatures, chemicals or other hazards. This advantage can prove particularly advantageous in environments that may expose cables to extreme temperatures or conditions where chemicals or other contaminants could pose risk.
How Does a Double Compression Cable Gland Work?
A double compression cable gland uses two seals to secure its cable. The first seal can be created by compressing either neoprene or EPDM rubber seal around the cable jacket to provide strain relief and stop it from pulling out of the gland. This provides strain relief and prevents the cable from pulling out of the gland.
The second seal is created by compressing a second rubber seal around the inner sheath of the cable. This not only provides additional strain relief but also creates a watertight seal around the cable, protecting it from moisture and other contaminants.
What is the Use of Double Compression Cable Gland?
There are several reasons why you might choose to use a double compression cable gland in your electrical installation:
1. Increased protection
As mentioned earlier, a double compression gland provides an additional layer of protection against moisture, dust, and other contaminants. This makes it ideal for use in harsh environments where cables are exposed to extreme temperatures, chemicals, and other hazardous conditions.
2. Improved safety
By providing a secure and watertight seal around the cable, a double compression gland reduces the risk of electrical shock and fire hazards.
3. Longer lifespan
Double compression glands are designed to last for many years, even in harsh environments. This means that you won’t have to replace them as often as you would with other types of glands, saving you time and money in the long run.
4. Versatility
Double compression glands can be used with a wide range of cables, making them a versatile option for many different types of electrical installations.
5. Easy installation
Double compression glands are easy to install, even for those with limited experience in electrical work. They come with simple instructions and can be installed in a matter of minutes.
Double Compression Cable Gland Applications
These cable glands are commonly used in a variety of applications, including:
1. Industrial automation
Double compression cable glands are commonly used in industrial automation applications to protect cables from water, dust, and other environmental hazards.
2. Marine applications
In marine applications, double compression cable glands are used to protect cables from saltwater and other harsh environmental conditions.
3. Power generation
Double compression cable glands are used in power generation applications to protect electrical cables from moisture and other environmental hazards.
4. Telecommunications
Double compression cable glands are used in telecommunications applications to provide a secure and reliable seal around cables.
5. Oil and gas
Double compression cable glands are commonly used in the oil and gas industry to protect cables from harsh environmental conditions.
6. Transportation
Double compression cable glands are used in transportation applications to protect cables from vibration, moisture, and other environmental hazards.
7. Construction
Double compression cable glands are used in construction applications to protect cables from moisture and other environmental hazards.
Overall, double compression cable glands are used in any application where a secure and reliable seal is needed around cables.
Different Parts of Double Compression Cable Glands
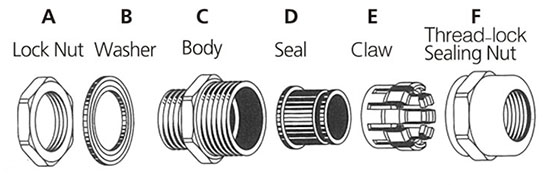
Double compression cable glands consist of several parts, each with a specific function. Here are the main parts of a double compression cable gland:
1. Body
The body of the gland is typically made of metal or plastic and provides the main structure for the gland. It also houses the compression seals and any other internal components.
2. Compression seals
Double compression cable glands have two compression seals, which are typically made of rubber or silicone. The compression seals are responsible for creating a secure seal around the cable to prevent the ingress of dust, water, or other environmental hazards.
3. Locknut
The lock nuts is used to secure the cable gland to the surface or enclosure where it is being mounted. It also helps to ensure that the gland is properly aligned with the cable entry point.
4. Sealing washer
The sealing washer is typically made of rubber or silicone and is used to provide an additional layer of protection against moisture and other environmental hazards.
5. Earth tag
The earth tag is used to provide a connection point for grounding the cable. It is typically made of metal and is attached to the body of the gland.
6. Entry thread
The entry thread is the part of the gland that is used to attach the gland to the enclosure or surface where the cable is entering. It is typically threaded to provide a secure fit.
7. Clamping ring
The clamping ring is used to secure the cable within the gland. It is typically made of metal and is tightened to compress the compression seals around the cable.
These are the main parts of a double compression cable gland, but there may be other components depending on the specific design and application of the gland.
Difference Between Single and Double Compression Gland
Single compression gland and double compression gland are two types of cable glands used in electrical and electronic installations to provide a secure seal between the cable and the enclosure or the equipment.
A single compression gland has a single compression seal that is formed by tightening the gland nut onto the cable. The compression seal is achieved by a cone-shaped rubber washer that compresses against the cable as the gland nut is tightened. Single compression glands are generally less expensive than double compression glands and are suitable for applications where the ingress protection requirement is not very high.
On the other hand, a double compression gland has two compression seals, one at each end of the gland. The first seal is formed by a cone-shaped rubber washer that compresses against the cable as the gland nut is tightened. The second seal is formed by a separate rubber washer that is compressed against the first seal as the gland nut is further tightened. Double compression glands provide a higher level of ingress protection compared to single compression glands and are suitable for applications where the environment is harsh or where the cable is exposed to vibration.
Single Compression Vs Double Compression Cable Gland
| Single Compression Cable Glands | Double Compression Cable Glands |
|---|---|
| Use a single compression seal to secure the cable | Use two compression seals to secure the cable |
| Provide basic protection against dust and moisture | Provide enhanced protection against dust, moisture, and other environmental hazards |
| Typically used in low-risk applications | Typically used in high-risk applications where a more secure seal is needed |
| Easy to install and remove | More complex to install and remove |
| Less expensive | More expensive |
| Suitable for use with most types of cables | Suitable for use with a wide range of cables, including armored and unarmored cables |
| May require additional sealing materials, such as O-rings or gaskets, for a secure seal | Generally do not require additional sealing materials |
| May not be suitable for use in harsh or corrosive environments | Designed to withstand harsh and corrosive environments |
How Many Types of Cable Glands Are There?
There are several types of cable glands available, and they can be categorized based on their design and application. Here are some common types of cable glands:
1. Compression cable glands
These are the most common type of cable glands and are used to create a seal around the cable by compressing the gland onto the cable.
2. Armored cable glands
These are designed to provide a seal around armored cables, which have a protective layer around the cable.
3. Flameproof cable glands
These are designed to provide a seal around cables that are used in hazardous areas and are required to be flameproof.
4. Hazardous area cable glands
These are designed to provide a seal around cables that are used in hazardous areas and prevent the spread of hazardous materials.
5. ATEX-approved cable glands
These are designed to be used in environments where there is a risk of explosion, and comply with the European ATEX directive.
6. EMC cable glands
These are designed to prevent electromagnetic interference (EMI) from affecting the equipment or cables.
7. IP-rated cable glands
These are designed to provide protection against dust and water ingress and are rated according to the IP (Ingress Protection) standard.
8. Ventilated cable glands
These are designed to allow air to flow through the gland, preventing the buildup of moisture.
9. Non-metallic cable glands
These are made from non-metallic materials, such as plastic or rubber, and are used in applications where metal may not be suitable, such as in corrosive environments.
These are some of the common types of cable glands available, but there may be other types that are designed for specific applications.
What is A1 and A2 cable gland?
A1 and A2 cable glands are designations used to specify certain types of cable glands in accordance with the European standard EN 50262. These designations refer to the dimensions and characteristics of the cable gland and indicate the size of the cable that the gland can accommodate.
A1 and A2 cable glands are typically used for non-armored cables, such as those made of PVC, rubber, or silicone. Here’s a breakdown of what these designations mean:
1. A1 cable gland: This type of cable gland is designed to accommodate cables with an outer diameter ranging from 2 mm to 18 mm. It has a single compression seal and is typically used in low-risk applications.
2. A2 cable gland: This type of cable gland is designed to accommodate cables with an outer diameter ranging from 5 mm to 32 mm. It has two compression seals, providing enhanced protection against environmental hazards, and is typically used in high-risk applications.
A1 and A2 cable glands are commonly used in industrial and commercial applications and are often specified in electrical designs and specifications. It’s important to select the right size and type of cable gland for your application to ensure a secure and reliable connection.
Conclusion
A double compression cable gland is an essential component of any electrical installation where cables need to be securely and safely connected. By providing an additional layer of protection against moisture, dust, and other contaminants, double compression glands can help to prolong the lifespan of your electrical equipment while reducing the risk of electrical shock and fire hazards. If you’re looking for a reliable and versatile cable gland for your next electrical installation, a double compression gland is definitely worth considering. With their easy installation, long lifespan, and improved safety features, they’re a smart choice for any electrician or DIY enthusiast.
Read Also:






