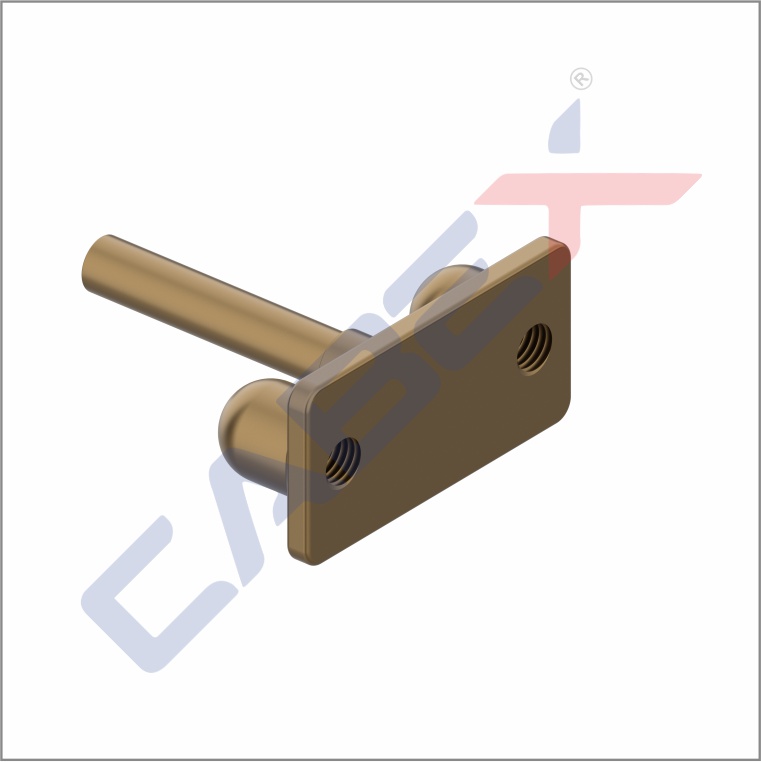
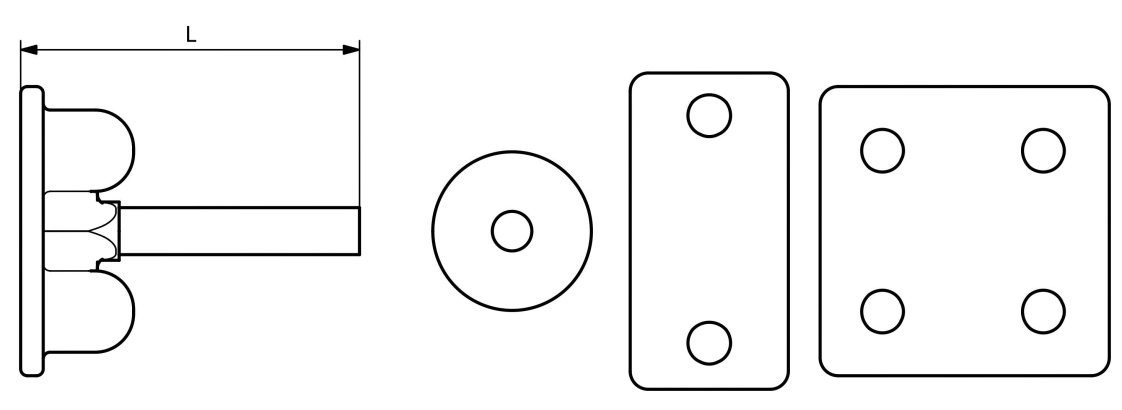
EARTH BONDING POINTS
Description
Earth bonding points, also known as grounding points or earthing points, are locations in an electrical or electronic system where components are connected to the Earth (ground) for safety and operational purposes. The primary functions of earth bonding points are:
Safety: Earth bonding helps protect people and equipment from electrical faults and lightning strikes. It provides a low-resistance path for electrical current to dissipate into the ground, preventing electrical shock hazards and reducing the risk of fires.
Noise Reduction: In electronic circuits, grounding can help reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) by providing a reference point for signals and eliminating common-mode noise.
Static Discharge: Earth bonding points are essential for dissipating static electricity that can build up on equipment or within electronic components. This is crucial in environments where sensitive electronics are present.
| #Holes | Hole Size (mm) | Plate Size (mm) | Stem Dia (mm) | L (mm) | Unit Weight (Kg) | Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M10 x 18 | 38 x 38 | 10.7 | 75 | 0.14 | EBP01 |
| 2 | M10 x 18 | 70 x 35 | 10.7 | 75 | 0.29 | EBP02 |
| 4 | M10 x 18 | 63 x 63 | 10.7 | 75 | 0.54 | EBP04 |


