Lightning is unpredictable, but its impact is devastating—damaging buildings, electrical systems, and appliances immediately. What really happens in the event of a surge strike? It can cause more expensive failures, unwanted downtime, and fire hazards as well. Is it possible to prevent this? A Lightning Arrester is not a luxury! It stops the direct strikes from the telecommunication pole high-voltage to the sensitive electronic equipment by diverting the flow of the current.
⚠️ Don’t Compromise on Safety! Get Certified Explosion Proof Cable Glands Now! ⚠️
In critical industrial zones, a faulty cable gland can lead to disastrous failures. Protect your assets, personnel, and compliance with our trusted, certified explosion proof cable glands.
- ⚡️ Instant protection against fire, dust, and moisture
- ✅ Certified by ATEX, IECEx, and PESO for global standards
- 🛠️ Engineered for toughest industrial environments
- 🚀 Limited stock! Ensure your safety today and avoid downtime
🎯 Act Now! Click below to secure the safest cable glands for your project BEFORE it’s too late:
👉 Get Explosion Proof Cable Glands
👉 See Industrial Cable Glands
👉 Explore Comprehensive Explosion Protection
What is a Lightning Arrester?
It is mainly a device. A lightning arrester mitigates a high-voltage spike caused by lightning flashes, switching, or impulse overvoltages. It is positioned between power lines and the ground to protect electrical infrastructure, such as substations, transformers, and transmission lines. Lightning arresters are frequently utilized in buildings, industrial facilities, and power distribution networks to improve system reliability.
Working of a Lightning Arrester
The function of a Lightning arrester is to protect against hazardous electric surges by safely discharging them to the ground. Once lightning or switching surge traveling waves reach it, the arrester produces a low-impedance pathway between power lines and the ground. It creates an electrical discharge at the preset breakdown voltage. The surge impedance of the line serves to control discharge as it regulates surge current flow. The arrester stays non-conductive when in normal operation, yet it turns conductive instantaneously after surge occurrence. When the overvoltage discharges, the arrester becomes highly resistant and stops new currents from flowing.
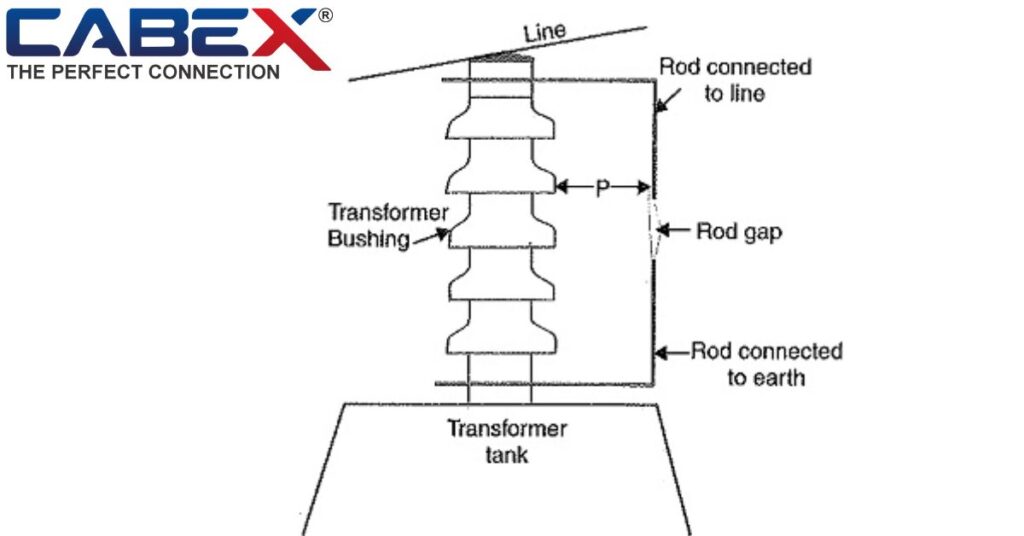
Lightning Arrester’s location
The best defense against high-voltage surges for electrical and communication systems requires the strategic placement of a lightning arrester. It is located as close as feasible to the equipment it protects to provide a low-resistance path for surge dissipation.
Locations for Lightning Arresters
1. Overhead Power Lines
It is installed on transmission towers and poles to prevent lightning strikes from damaging distribution circuits, high-voltage transmission lines, and service drops. It helps avoid power outages and line flashovers in the event of surges.
2. Transformers
It protects the low-voltage coil against abrupt voltage spikes and is used on distribution, pole-mounted, and pad-mounted transformers. It prolongs the transformer’s lifespan and guarantees continuous functioning from spikes in voltage.
3. Switchgear
It is installed in substations on circuit breakers, disconnect switches, and bus bars to guard against switching surges and overvoltages caused by lightning.
4. Generators and Motors
It is positioned at cable boxes, bearing housings, and stator windings to guard against damage from brief surges. In industrial settings where power systems depend on motors and generators, it is indispensable.
5. Buildings
It is placed at the main service entrance to protect appliances and electrical wiring from surges caused by lightning. It guards against appliance malfunctions and electrical fires.
6. Lines of Communication
It is used at interfaces for data cables and telephones where lines of communication enter or leave buildings. It guards against power surges damaging communications equipment.
Types of Lightning Arrester
A lightning arrester safeguards electrical systems by safely directing high-voltage surges to the ground. Although they differ in construction, they serve the same purpose.
1. Horn Gap Arresters
2. Multi-Gap Arresters
3. Valve-Type Arresters
4. Pellet-Type Arresters
Characteristics of an Ideal Lightning Arrester
The perfect lightning arrester should preserve system stability and lifespan while offering dependable surge protection.
1. Under typical voltage circumstances, the arrester must continue to be non-conductive, which means it cannot leak current or obstruct the transmission of power. Even with slight variations, its spark-over voltage needs to be greater than the maximum system voltage.
2. It ought to respond nearly instantly to brief overvoltages brought on by switching surges or lightning strikes. In order to safely discharge excessive voltage to the ground, the arrester must establish a low-impedance channel.
3. The arrester should be able to withstand strong surge currents—which might occasionally exceed tens of kiloamperes—without suffering any harm. In order to preserve its protective function and keep the system from experiencing undue voltage stress, it must endure repeated surges.
4. If the transient voltage drops below the breakdown threshold, the arrester ought to cease operating immediately. It must provide system stability and minimize needless energy losses by stopping follow-up power frequency currents from continuing.
Why Choose Cabex for Lightning Arresters?
For residential, commercial, and industrial applications, Cabex India provides excellent lightning protection solutions that guarantee safety, dependability, and adherence to industry standards.
1. The manufacturing company Cabex India produces high-quality Lightning Protection Accessories, industrial Cable Lands, and Earthing Accessories that offer peak operational safety standards.
2. Our company protects buildings, power systems and delicate equipment with lightning rods alongside grounding systems and surge protection devices from harmful voltage surges.
3. We offer low-resistance grounding systems that serve as an effective release mechanism for electrical surges to protect electrical infrastructure.
4. Our experts install lightning protection systems for commercial, industrial and residential buildings based on international safety requirements.
5. Our state-of-the-art production techniques and rigorous quality control systems ensure the production of a durable lightning arrester that will last for a long time.
6. Cabex India’s joint operating entities should be considered first for lightning protection solutions because we deliver specialized professional help alongside customized solutions and expert advisory services.
Conclusion
To safeguard infrastructure and electrical systems against damaging surges, lightning arresters are essential. For optimal safety and longevity, Cabex India provides dependable, high-quality lightning protection solutions. Through stringent quality inspections, we guarantee accuracy, compliance, and client satisfaction in our state-of-the-art 25,000-square-foot facility with a highly qualified technical staff. Our one-stop shop serves power plants, railroads, oil and gas, electrical, and other industries. For unparalleled dependability and excellent lightning protection, rely on Cabex.
FAQ’s:
1. What attracts lightning?
Lightning pursues the route of least resistance to the ground rather than being “attracted” to certain things. On the other hand, conductive materials, big buildings, and metal items can make a strike more likely.
2. How do you connect a lightning arrester?
A lightning arrester protects devices connected in parallel. It is usually placed between the power line and the earth at substations, transformers, and buildings.
3. Do lightning strikes in AC or DC?
Lightning behaves differently than typical AC or DC. It is made up of an electrical charge that surges quickly, known as a high-energy impulse signal.
4. What causes lightning arresters to malfunction?
Dielectric failure, overvoltage stress, contamination, poor maintenance, or aged components that impair the device’s capacity to deflect surges efficiently can all lead to failure.
5. How do lightning arresters safeguard electricity systems?
The arrester dissipates excess energy and keeps electrical equipment safe by offering a low-resistance path to the ground in the case of a voltage surge.
Follow us:- Facebook, Instagram
You May Also Like: Comprehensive Cable Gland Size Chart for Your Needs , How to Identify Genuine Quality Brass Cable Glands Easily





